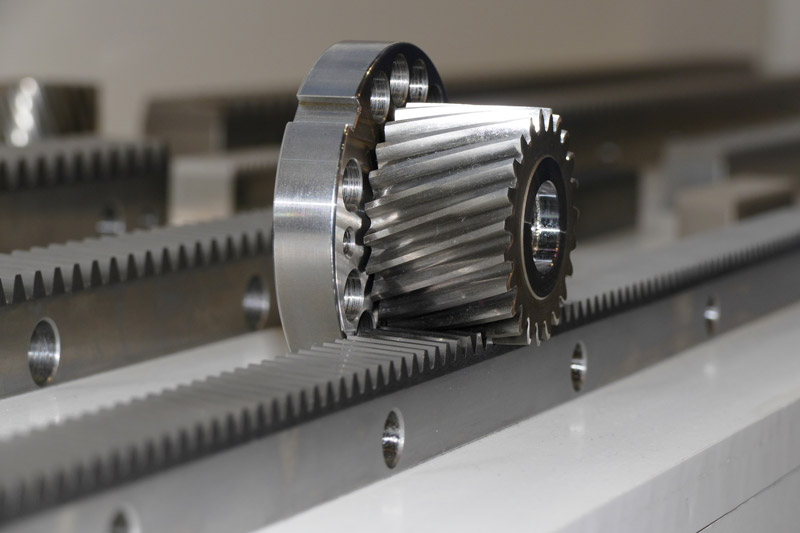
Spur gears and racks
Spur gears
Spur gears are components used for the transmission of rotary motion between parallel or intersecting shafts. They consist of two or more toothed wheels, called pinions, with teeth cut or machined around their circumference. These gears are called “spur” because their outer surface has a cylindrical shape.
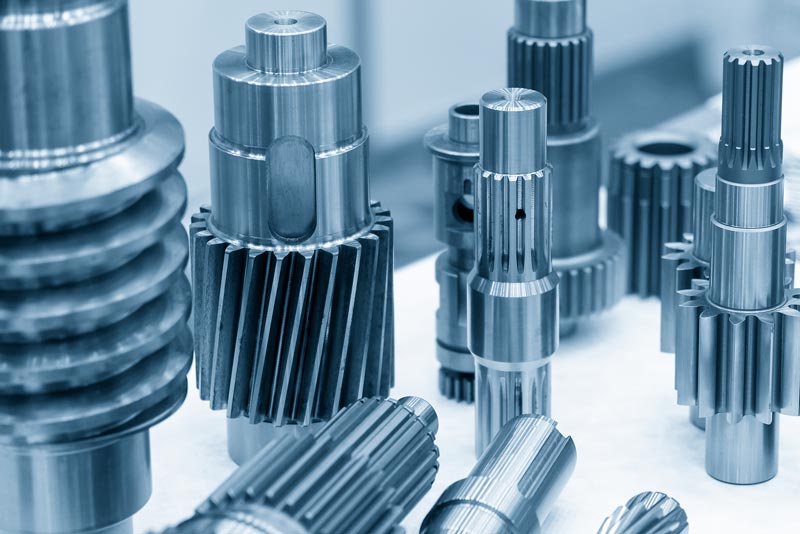



The production of spur gears
The production of spur gears is a process that involves several steps and specialised techniques to obtain gears with precise design and quality specifications. The process begins with the design of the gears, which involves defining technical specifications such as module, number of teeth, pressure angle, type of tooth profile, tolerances and other characteristics. The most common production method for spur gears is cutting.
This is followed by grinding, a critical step in order to ensure precise tolerances and an optimum surface finish. Gears can be subjected to heat treatments such as hardening and tempering to improve the strength and hardness of the materials. Throughout the production process, stringent quality controls are necessary to ensure that the gears meet specific requirements.
Racks
Rack and pinion gears, often simply called “racks”, are a component used to transmit linear motion.
Unlike spur gears, which transmit rotary motion, racks are designed to convert rotary motion into linear motion or vice versa. A rack is a rectangular or profiled bar with a continuous toothed surface along its length. The teeth of the rack are generally cut or machined through milling along a straight line and these teeth align with those of a gear wheel known as a pinion.
Racks are designed to be wear resistant and have a good load bearing capacity. Their operation is smooth and linear, making them ideal for many applications where rotary motion needs to be transformed into linear motion or vice versa.
